Introduction
Spaying, also known as ovariohysterectomy (OHE) or ovariectomy (OVE), is a common surgical procedure performed on female cats (queens) to prevent estrus, unwanted pregnancies, and various health issues. This comprehensive guide covers the indications, benefits, surgical techniques, and frequently asked questions about spaying cats to help pet owners make informed decisions.
Why Spay Your Cat?
Spaying is not only about preventing unwanted litter; it also offers numerous health and behavioral benefits. Here are some key reasons to consider spaying your cat:
Health Benefits of Spaying
- Mammary Tumors: Spaying before the first heat cycle eliminates the risk of mammary tumors by up to 91%.
- Elimination of Pyometra Risk: Pyometra, a life-threatening uterine infection, is common in unspayed cats.
- Control of Reproductive Disorders: Prevents uterine, ovarian, and vaginal neoplasia, cysts, and congenital anomalies.
- Management of Endocrine and Dermatological Issues: Helps control conditions like diabetes and certain skin diseases.
Indications for Spaying in Cats
Spaying is recommended for the following reasons:
1. Prevention of Estrus and Unwanted Pregnancies
- Eliminates heat cycles, which can be noisy and stressful for the cat and the owner.
- Prevents unwanted litter, reducing the burden of overpopulation.
2. Prevention of Reproductive Diseases
- Mammary Tumor in cats: Spaying before the first heat significantly eliminates the risk.
- Pyometra: A life-threatening infection of the uterus that commonly affects unspayed cats.
- Uterine and Ovarian Neoplasia: Removes the risk of cancerous growth in the reproductive organs.
3. Treatment of Existing Conditions
- Pyometra: Emergency spaying is often required to treat this condition.
- Uterine or Vaginal Prolapse: Surgical intervention is necessary to correct these abnormalities.
- Uterine Torsion or Trauma: Spaying is performed to address these life-threatening conditions.
4. Management of Congenital Anomalies
- Corrects abnormalities such as uterine or vaginal malformations.
5. Control of Endocrine and Dermatological Disorders
- It helps manage conditions like diabetes and certain skin diseases.
Considerations in spaying in cat
1 Preoperative considerations
- HCT (Hematocrit)
- TP ( total protein)
- In patients >5–7 y, consider electrolytes, liver enzymes, BUN, and Cr
Premedication
- Diazepam (0.2 mg/kg IV)
- Hydromorphone (0.05–0.2 mg/kg IV, IM in dogs; 0.05–0.1 mg/kg IV, IM in cats)
2 Intraoperative considerations
Induction
If premedicated, give: • Propofol (2–4 mg/kg IV), or • Alfaxalone (2–3 mg/kg IV)
If not premedicated, give: • Propofol (4–8 mg/kg) IV), or • Alfaxalone (2–5 mg/kg IV)
Maintenance
Isoflurane or sevoflurane, plus
Fentanyl (2–10 µg/kg IV PRN in dogs; 1–4 µg/kg IV PRN in cats) for short-term pain relief, plus
Hydromorphone (0.05–0.2 mg/kg IV PRN in dogs; 0.05–0.1 mg/kg IV PRN in cats) , plus
Ketamine (low dose; 0.5–1 mg/kg IV),
Fluid needs
Estimated blood loss(EBL)
- 5–10 mL/kg/h plus 3× EBL
- 10–20 mL/kg/h plus 3× EBL if open abdomen
Monitoring
- Blood pressure
- HR
- ECG
- Respiratory rate
- SpO2
- Temperature
- EtCO2
3 Postoperative Considerations
Analgesia
- Carprofen (2.2 mg/kg q12h PO), or
- Deracoxib (3–4 mg/kg q24h for <7 days PO), or
- Meloxicam (0.1–0.2 mg/kg once SC, PO then 0.1 mg/kg PO q24h)
Monitoring
- SpO2
- Blood pressure
- HR
- Respiratory rate
- Temperature
Surgical Techniques for Spaying
Pre-Surgical Preparation
- Incision Site:
- The incision is made in the middle third of the caudal abdomen for cats, as the uterus is more caudal compared to dogs.
- Incision Length: 2-4 cm through the skin and subcutaneous tissue to expose the linea alba.
Step-by-Step Procedure
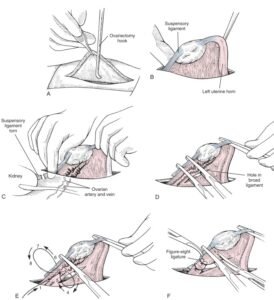
- Exteriorization of the Uterine Horn:
- Use an OVE hook to locate and elevate the uterine horn.
- Identify the suspensory ligament and stretch it to exteriorize the ovary.
- Ligation of the Ovarian Pedicle:
- Place clamps (Mosquito, Crile, or Rochester-Carmalt) across the ovarian pedicle.
- Apply absorbable sutures (e.g., PDS, Maxon, Vicryl) in an encircling or figure-eight pattern.
- Transection and Removal:
- Transect the ovarian pedicle and remove the ovary.
- Repeat the procedure on the opposite side.
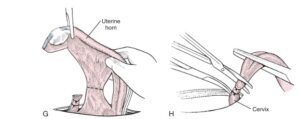
- Uterine Body Ligation (for OHE):
- Ligate the uterine body cranial to the cervix using figure-eight or circumferential sutures.
- Transect the uterine body and ensure hemostasis.
- Closure:
- Close the abdominal wall in three layers: fascia of the abdomen
- linea alba
- subcutaneous tissue
- skin.
Images of procedure
Alternatives to Spaying
While spaying is the most effective method for preventing reproduction, alternative options include:
Medical Prevention (Megestrol Acetate) in Dogs
- Anestrous stage: 0.55 mg/kg PO q24h for 32 days
- Proestrus stage: 2.2 mg/kg PO q24h for 8 days
Medical Termination
Prostaglandin F2α (Lutalyse)
- Cats:
- 2 mg/cat IM q24h for 5 days
- Start at least 30 days after breeding
Cloprostenol (Estrumate)
- Dogs:
- 1–2 µg/kg SC q24h for 5–7 days, starting at least 30 days after breeding
- OR 1 µg/kg SC q48h for 3 doses + Cabergoline (Dostinex) (5 µg/kg PO) q24h for 9 days
Cabergoline (Dostinex)
- Dogs: 1.65 µg/kg SC q48h for 5 days (efficacy depends on timing with LH surge)
Bromocriptine (Parlodel)
- Dogs:
- 0.1 mg/kg/day PO for 6 days (starting day 35 of gestation)
- OR 0.03 mg/kg PO q12h for 4 days (after day 30 of gestation)
Mifepristone (Mifeprex)
- Dogs: 2.5 mg/kg PO daily for 4–5 days (starting day 32 of gestation)
Aglepristone (Alizine, Alizin)
- Dogs:
- 10 mg/kg SC, given twice q24h
- OR 0.15 mg/kg SC given twice q24h
- Cats:
- 15 mg/kg SC q24h for 2 days (starting day 33)
However, these methods may have side effects and are less reliable than surgical spaying.
FAQs About Spaying in Cats
1. What is the best date for spaying?
The ideal age for spaying is before the first heat cycle, typically around 4-6 months of age.
2. How long does it take for a cat to recover after spaying?
Most cats recover within 7-10 days. Ensure they avoid strenuous activity and keep the incision site clean.
3. Are there any risks associated with spaying?
Spaying is a safe procedure, but like any surgery, it carries risks such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
4. Can spaying cause weight gain?
Spaying may slow down metabolism, but weight gain can be managed with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
5. Is spaying beneficial for older cats?
Yes, spaying can still prevent pyometra and mammary tumors in older cats, though the risks of surgery may be higher.
Comparison: Ovariohysterectomy vs. Ovariectomy
| Aspect | Ovariohysterectomy (OHE) | Ovariectomy (OVE) |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Removal of ovaries and uterus | Removal of ovaries only |
| Indications | Pyometra, uterine neoplasia | Prevention of estrus |
| Recovery Time | 7-10 days | 7-10 days |
| Complications | Slightly higher risk | Lower risk |
Modern Viewpoint on Spaying Cats
Spaying, or ovariohysterectomy, involves the surgical removal of a female cat’s ovaries and uterus to prevent reproduction. In recent years, the perspective on spaying cats has evolved, shaped by advances in veterinary science, animal welfare priorities, and ethical considerations. This practice remains a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership, but modern discussions reflect a nuanced balance of health benefits, population control, potential risks, and emerging alternatives. Below is an exploration of the contemporary viewpoint on spaying cats, emphasizing its role in feline health and societal well-being.
Population Control and Animal Welfare
A primary driver of spaying is the urgent need to address cat overpopulation. Millions of stray and feral cats worldwide face starvation, disease, or euthanasia due to uncontrolled breeding. Spaying prevents unwanted litters, significantly reducing the number of cats entering shelters or living on the streets. Programs like Trap-Neuter-Return (TNR) have gained traction, focusing on spaying feral cats to stabilize colony sizes humanely. These initiatives align with modern animal welfare principles, emphasizing compassionate solutions over culling. By spaying kittens as early as 8–12 weeks, TNR programs and shelters curb population growth effectively, reflecting a societal commitment to reducing feline suffering.
Health Benefits of Spaying
Veterinary science underscores the health advantages of spaying. When performed before the first heat cycle (around 6 months), spaying drastically lowers the risk of mammary cancer, a malignant disease in cats. It also eliminates the possibility of pyometra, a potentially fatal uterine infection. Additionally, spaying prevents ovarian and uterine tumors, which, though rare, can occur in intact females. Behaviorally, spayed cats avoid the stress and risks associated with heat cycles, such as yowling, restlessness, or escaping to find mates. These benefits improve the quality of life for indoor cats and reduce owner challenges, making spaying a standard recommendation in veterinary practice.
Risks and Considerations
Despite its benefits, recent research has highlighted potential downsides to spaying, prompting a more tailored approach. Early spaying (before 12 weeks) may increase the risk of obesity, urinary tract issues, or orthopedic problems in some cats, as hormones play a role in growth and metabolism. Large breeds, like Maine Coons, may benefit from slightly delayed spaying to allow skeletal development. However, the risks of delaying spaying, such as unintended pregnancies or mammary cancer, often outweigh these concerns. Veterinarians now advocate for individualized timing, considering factors like breed, lifestyle, and health status. Post-surgical care, including weight management, also mitigates long-term risks, reflecting a modern emphasis on personalized veterinary medicine.
Ethical and Cultural Perspectives
The ethics of spaying have sparked debate in some circles. Spaying involves removing healthy organs, leading some owners to question its necessity, particularly in non-breeding pets. Cultural attitudes vary, with certain communities viewing sterilization as unnatural or contrary to traditional values. In response, researchers are exploring alternatives like ovarian-sparing surgeries, which preserve hormonal functions while preventing reproduction, or chemical sterilization methods, such as injectable contraceptives. These options are not yet widely available, but they signal a shift toward addressing ethical concerns while maintaining population control. Public education campaigns also play a role, promoting spaying as a responsible choice that enhances animal welfare.
Evolving Practices and Future Directions
Minimally invasive procedures, like laparoscopic spaying, reduce recovery time and pain, though they are costlier and less common. Research into non-surgical sterilization continues, with potential for scalable solutions that could transform feline population management. Additionally, genetic studies are shedding light on how spaying affects long-term health, informing guidelines on optimal timing. The modern viewpoint embraces these innovations, aiming to balance immediate needs with long-term feline health.
Conclusion
Spaying is a vital procedure for ensuring the health and well-being of female cats. It not only prevents unwanted pregnancies but also reduces the risk of serious health conditions like pyometra and mammary tumors. By understanding the indications, surgical process, and benefits, pet owners can make informed decisions for their feline companions.
Note
Always consult a licensed veterinarian to determine the best approach for your cat’s specific needs.